Sexually transmittable infections/diseases (STI/STDs) are common. And while often associated with spots, sores, and warts that develop in the genital regions, they sometimes affect the mouth. In these cases, you may find it difficult to eat due to pain and the discomfort caused by the sores.
There are different types of STDs that can affect the mouth. Those manifesting as tongue symptoms are generally common, but these diseases can also cause symptoms on the gums and the inside of the cheeks. Let’s discuss.
What are the types of oral STDs?
The American Dental Association reports that each year, about 20 million people are diagnosed with an STD. Some of these STDs are localized to the genitals. Others, however, can cause a breakout of symptoms in your mouth. They include:
- Human papillomavirus
- HPV mouth warts
- Herpes
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
When it comes to STD mouth sores, oral herpes is generally considered the most common issue. Gonorrhea is a common reason for patients to experience STD symptoms in the mouth. A large number of these conditions, such as herpes, are not curable. This does not mean the condition cannot be treated. There are treatments that help to reduce the frequency and severity of herpes breakouts.
In some cases, however, effective treatments are available to get rid of the STD. This is mostly the case when a patient has an STD that is caused by bacteria and not a virus.
What are the symptoms of oral STDs?
There are different symptoms that can develop if a patient has an oral STD. Due to different STDs being able to affect the mouth, it’s important to understand how each looks and what the accompanying symptoms may be. If you suspect you might have an STD, you’ll need to see a doctor.
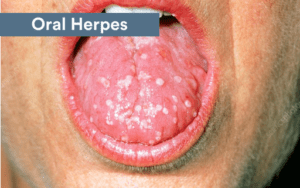
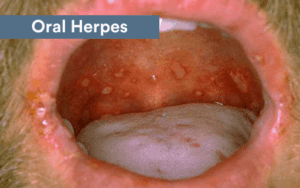
Herpes
Herpes is also called the herpes simplex virus. When this STD affects the genital region, it is likely the patient has herpes simplex virus type 2. In cases where the mouth is affected, the patient has herpes simplex virus type 1 usually.
Herpes simplex virus type 1 is known to cause cold sores in the mouth. While cold sores are common in patients with oral herpes, other types of lesions can also develop. The patient may experience breakouts when they have herpes. These breakouts may come and go. When the patient has a flare-up of the symptoms, it will look like blisters that develop in the oral cavity.
The blisters often affect the inside of the patient’s cheeks. These blisters can be different colors, including red, pink, gray, or yellow. Sometimes, the blisters appear clear. A breakout usually lasts for a week, up to 10 days.
Still need answers?
Book with a top-rated dentist in your city to get the treatment you need.
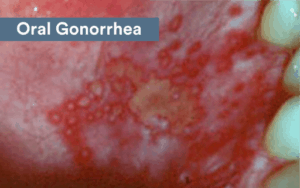
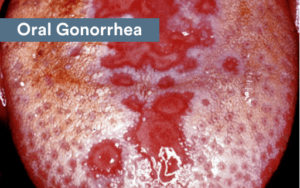
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is also a relatively common STD. This condition is caused by bacteria, unlike herpes that is related to a virus. When the bacteria enters the mouth, a bacterial infection may develop. The mucous membranes are the primary area of the mouth that will be affected by the bacterial infection. This is why symptoms may appear in the mouth, as well as the throat.
Many patients experience mild symptoms of gonorrhea. Gonorrhea in the mouth may develop slowly and not show any obvious signs at first. This is why it’s often difficult to detect the condition at an early stage.
A burning sensation may be experienced in the throat. Some people report the burning affecting their mouth too. Swollen glands are also common among people who have gonorrhea. In some cases, the tongue may be affected by white spots.
Syphilis
In the last 16 years, there’s been a significant increase in the prevalence of syphilis. This condition develops in phases. The initial phase will usually cause sores to develop inside the mouth. These syphilis symptoms in the mouth are called chancres.
The sores can develop at the tip of the patient’s tongue. Sometimes, they form on the gums or close to the tonsils. The lips may also be affected. The sores tend to grow larger over time and can turn into an open sore. The sore may be red, gray, or yellow.
Oral STD pictures
Some STDs can affect the tongue, while others may rather target the gums, back of the mouth, or the cheeks. Below, you will find some photos that show the appearance of STDs tongue symptoms.
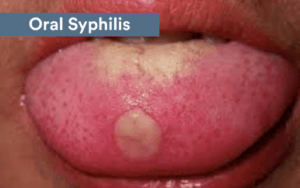
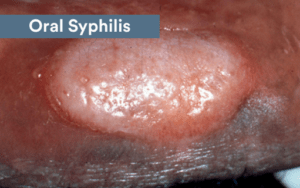
Source: ADA/ Mouthhealthy.org
How long do oral STDs take to show up?
The incubation period and time it takes STDs to start showing up differs. Some STDs can start to produce symptoms in a matter of days. Others, however, may take several years before any symptoms can be seen.
Still need answers?
Book with a top-rated dentist in your city to get the treatment you need.
Herpes tends to cause symptoms the fastest compared to other STDs that affect the mouth. When a person contracts oral herpes, symptoms usually start to show within two to 12 days.
With syphilis, it usually takes about three weeks before symptoms develop. Depending on the type of syphilis, some people may only experience symptoms after as many as 20 years.
How are oral STDs Diagnosed?
The diagnostic process starts with a few questions about sexual history and activity.
The doctor also needs to inspect the lesions or sores in the patient’s mouth. In most cases, a doctor will be able to determine the type of STD affecting a patient by looking at these sores.
The doctor may ask the patient to undergo a test. This can help to rule out other potential causes behind the sores, blisters, or spots. These tests can also help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis for the STD that affects the patient.
How are oral STDs treated?
Treatment depends on the STD the patient is diagnosed with. Some STDs cannot be cured, but treatment usually helps to slow down the progression of the disease. This is generally the case if the patient is diagnosed with a viral infection that spread through sexual activity. When bacteria cause the STD, then antibiotics can often be used as a treatment option.
Can I visit a dentist if I have an oral STD?
When you have an oral STD, you may fear finding a dentist near you. You may not be sure if the professional will refuse to provide services during the dentist appointment. Fortunately, this is not the case. Most dentists are capable of providing efficient dental services to patients who have oral STDs.
In fact, there are cases where the dentist may be able to detect the presence of an oral STD. Dentists are highly trained in identifying problems with the oral cavity. Thus, they are generally able to identify sores and other symptoms that signal the presence of an STD. The dentist may also advise you on appropriate ways to care for your mouth when there are sores.
Due for a checkup?
Find a top rated dentist near you that takes your insurance.
In cases where the symptoms are severe, the dentist may consider asking the patient to obtain adequate treatment for the STD before dental services are rendered. When the patient wants to find a dentist, they should understand that severe sores in the mouth may interfere with the dentist’s ability to perform root canals, extractions, and other procedures. Thus, the patient may need to wait for the flare to clear up at least a bit first.
Conclusion
Numerous sexually transmitted diseases can affect the oral cavity. This often occurs when the mouth is used during sexual intercourse. In these situations, warts, sores, and other symptoms may develop in the mouth. These symptoms may also lead to pain, discomfort, and irritation in the mouth.
Some STDs, such as syphilis, are also known to affect the teeth. Proper oral care is essential for people with STDs in their mouths. STD mouth sores can become aggravated when the patient does not obtain adequate treatment and fails to take better care of their dental health.







